 | Female Reproductive System | | |
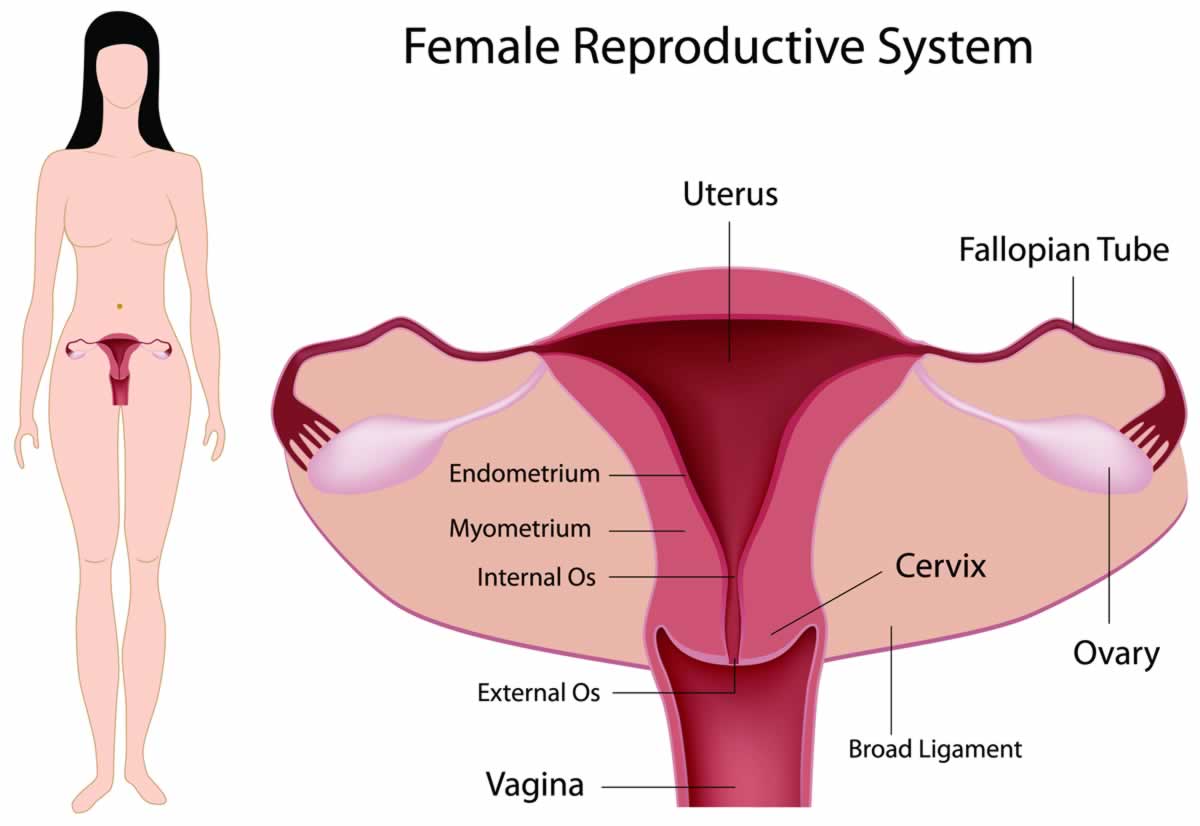
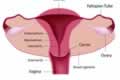
The female reproductive system consists of different parts like the Uterus, Fallopian tubes, Ovaries, Cervix, Vagina and the Vulva.
The main organ called the Uterus or the Womb is present in the lower part of the abdomen behind the urinary bladder and in front of the rectum.
From either side of the uterus originate tube like extensions called the Fallopian tubes, which end into a wide opening called the 'Fimbrial end'.
The female gland called the Ovaries are present one each, on either side of the womb near the fimbrial end of the Fallopian tubes.
The womb opens into vagina through an opening or the mouth called the 'Cervix', which is present at lower end.
From the cervix starts a canal called the Vagina, which opens to the outside through an opening called the 'Introitus', present between the thighs in the groin region, just below the urethra.
This opening is surrounded by fleshy folds called the 'Vulva', which are formed of two pairs of lip-like structures called the 'Labia minora' and the 'Labia majora'.
After puberty, the ovaries produce a fluid filled sac called the Follicle containing an egg.
Each month this follicle ruptures releasing the egg.
This egg is picked up by the fimbrial end of the Fallopian tube and transferred into the Fallopian tube.
During intercourse the male partner discharges semen-containing sperm into the female partners vagina.
These sperm from the vagina travel through the uterus into the Fallopian tube to fertilize the egg in the farthest one-third part of the fallopian tube.
The fertilized egg then travels through the Fallopian tube and enters the uterus, where it gets embedded into the wall of the uterus to further develop into a baby.
If the egg does not get fertilized then it is shed out of the vagina along with the disintegrated superficial lining of the uterus in the form of menstrual bleeding, during the monthly periods. | | 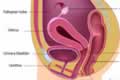 | Female Sexual Anatomy | | |
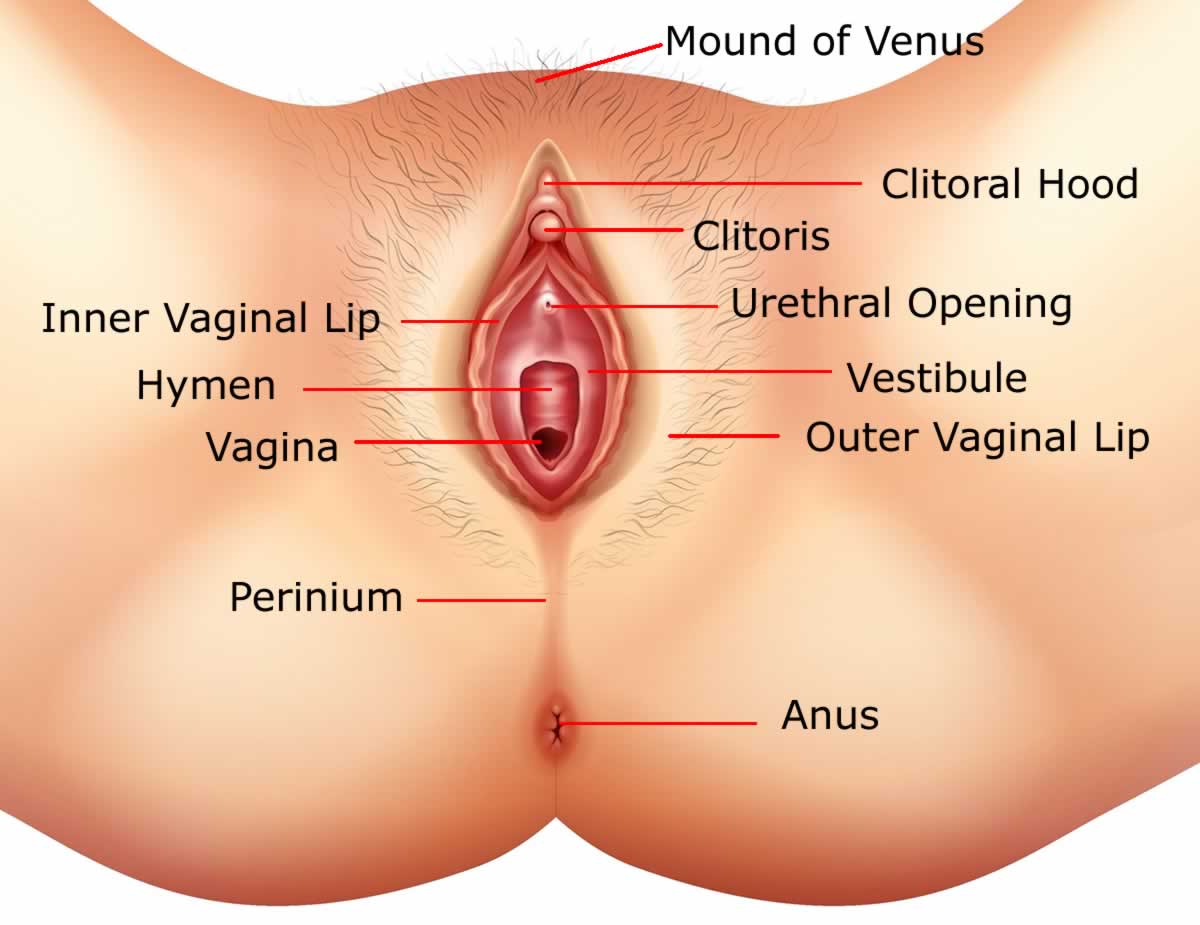
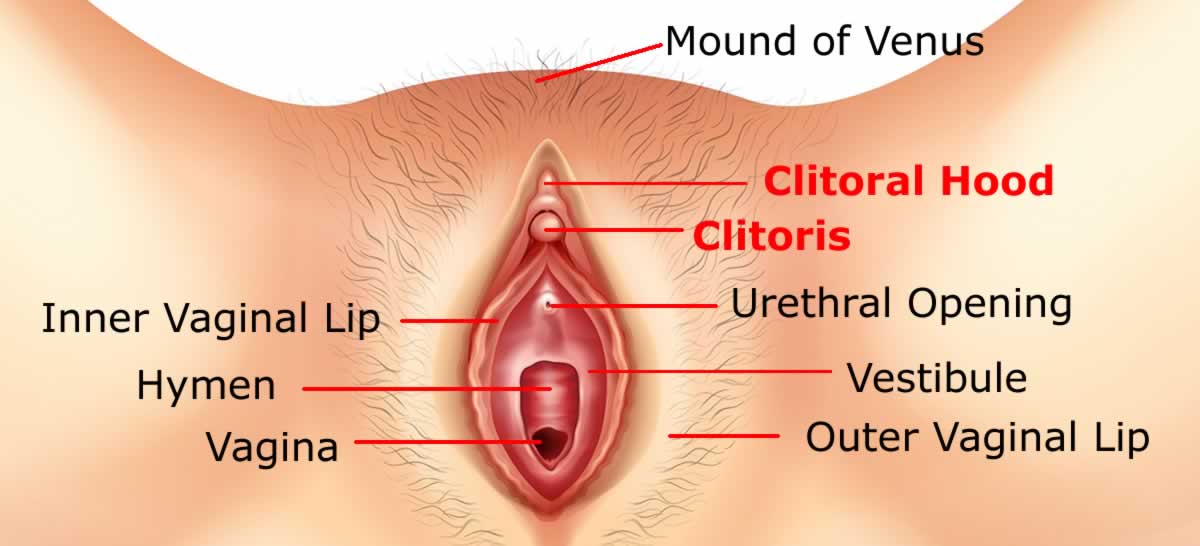
A woman has a special opening in the groin region called vagina.
The vaginal opening is covered externally by a membrane called hymen and placed behind the opening of urethra from where the urine is passed and in front of the anus from where human waste is excreted.
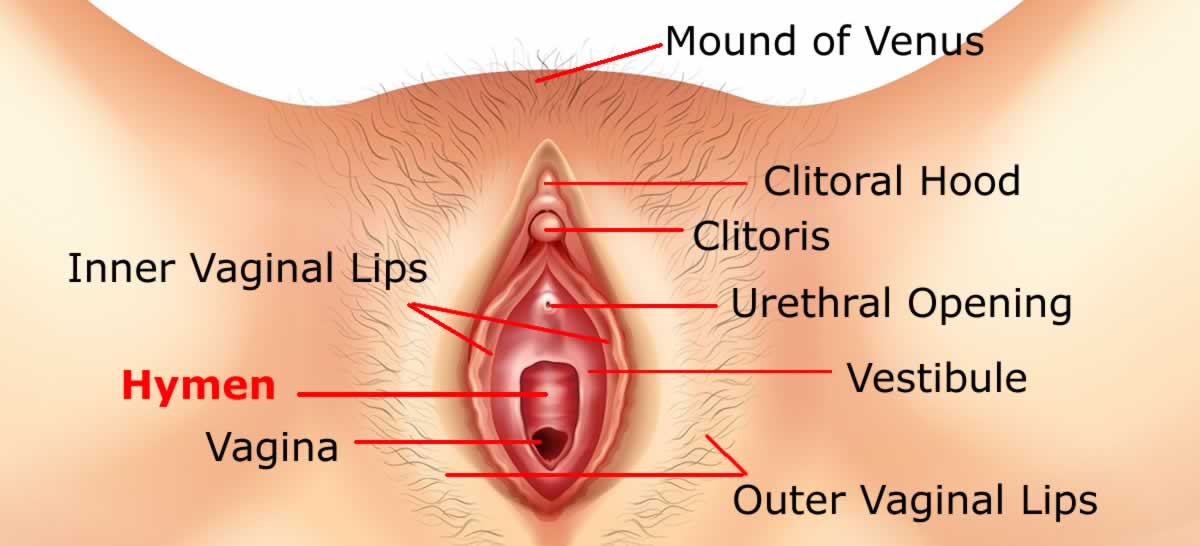
Girls have a small and less obvious external genital organ called Clitoris which is richly supplied by blood vessels and nerves and is very sensitive to touch. When stimulated it swells and becomes hard and gives a pleasurable feeling called orgasm.
The vaginal opening, clitoris and a separate opening for the passage of urine are protected by two lip like folds of skin called ‘Labia’.
The ‘outer larger lip’ consists of thick fold of skin to cover and protect other parts.
The top of the outer lip merges with the skin and hair on the pad of fatty tissues covering pubic bone referred as Mound of Venus.
The two smaller lips join at the top to form a protective hood over sensitive clitoris. They also protect the opening to the urethra.
The space below the smaller lips is called a vestibule.
The special glands under the skin folds secret a fluid which keeps the vaginal opening moist specially on sexual arousal (to facilitate intercourse.)
Girls do not ejaculate any secretion, but experience the increased secretion around vagina when they get aroused and lubricate if they are stimulated or have a sexy dream.
Vagina extends into a canal of 7 to 9 cm length surrounded by fibromuscular tissues, which remains collapsed and increases the space within during intercourse and childbirth.
The walls of the vagina are also well lubricated by its secretions during intercourse. Certain discharges from vagina are considered normal discharges which increase during ovulation and sexual arousal.
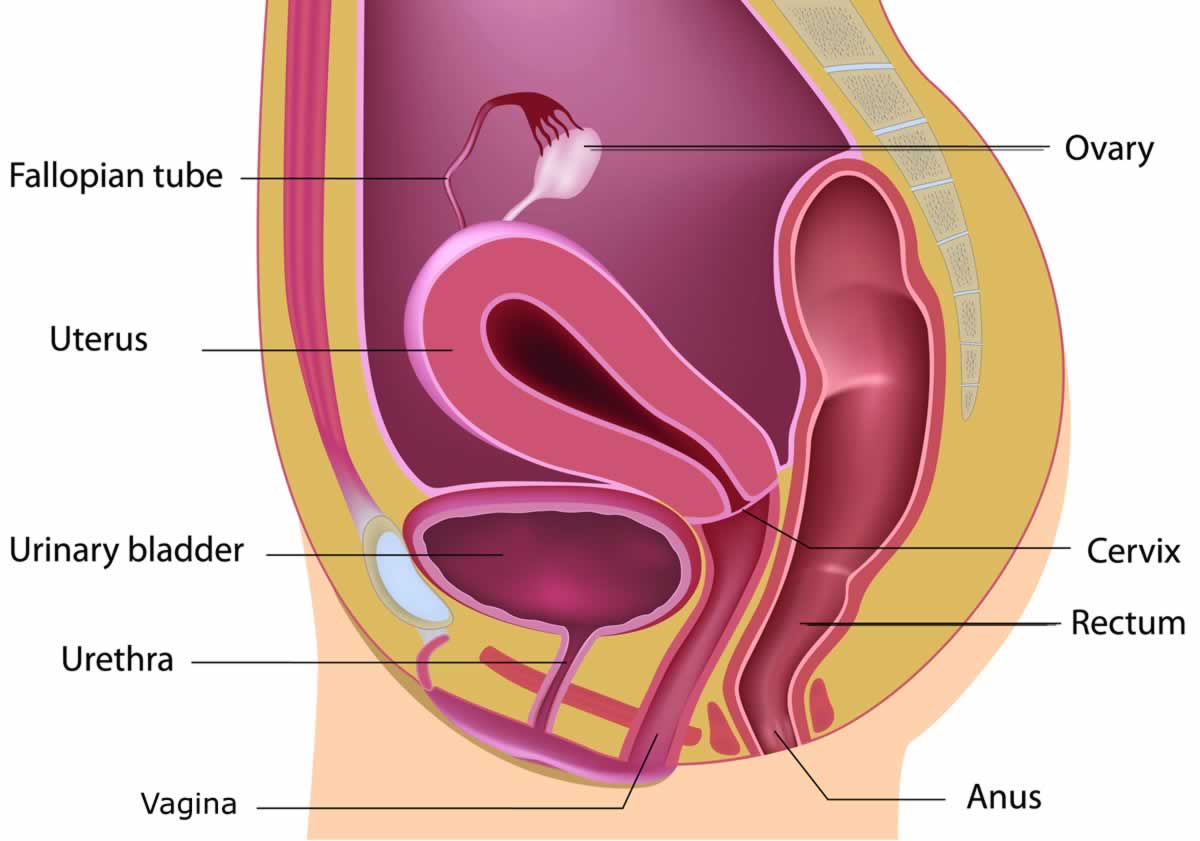
Upper end of vaginal canal is connected to a small hollow muscular bag called uterus which protects the developing baby. Uterus is suspended inside the pelvic bones with the help of strong muscle fibres and ligaments to bear the weight of the baby.
The narrow end of the uterus called cervix, opens into upper end of vaginal canal and the other broad side of uterus is in continuation of two hollow tubes called Fallopian tubes.
On either side of uterus are two Ovaries.
Vaginal deodorants:
Skin around vagina should be cleaned with soap and water. The smell of the body when clean is the natural. As this part is very delicate and sensitive use of deodorant or perfume may cause burning or itching.
| |  | External Sexual Organ - Clitoris | | |
The Clitoris is the most sensitive part of the female genitals, located toward the top of a woman’s external genitals and in front of the urethral opening above the point where two inner lips of vagina meet and is covered by outer lips of vagina.
The size and appearance of the clitoris vary among women and most part of the clitoris is inside and not visible. Only small button like part of the clitoral head is seen on lifting the folds of outer lip.
This head of the clitoris is also called ‘clitoral glans’, The skin of the inner lip around the clitoral head forms the “Clitoral Hood”. The part of the clitoris placed under the clitoral hood is called clitoral shaft, which branches inside as an inverted v-shaped extensions, called ‘crura’. The crura are connected to pelvic bone on either side.
Clitoris is richly supplied by nerve endings clitoris is highly sensitive to touch, pressure and temperature.
Being made of several erectile fibers, clitoris enlarges in size on touching and stimulation, which gives woman a pleasurable feeling.
Clitoris is the only anatomical organ in women, whose only function is to focus and accumulate sexual sensation and receive erotic pleasure.
Woman may stimulate the clitoris during self pleasuring and during intercourse if possible. During love making stimulation of clitoris may be done by the partner as part of foreplay or for achieving orgasm during intercourse, or as an after play.
Clitoral Circumcision
In women circumcision is done by surgical removal of the clitoral hood that exposes the head of the clitoris, i.e. clitoral glans.
This procedure is supposed to enhance sexual pleasure for women by allowing additional stimulation of clitoris.
However, exposing clitoral glans may make it more painful and irritating.
| |  | External Sexual Organ - mons pubis | | |
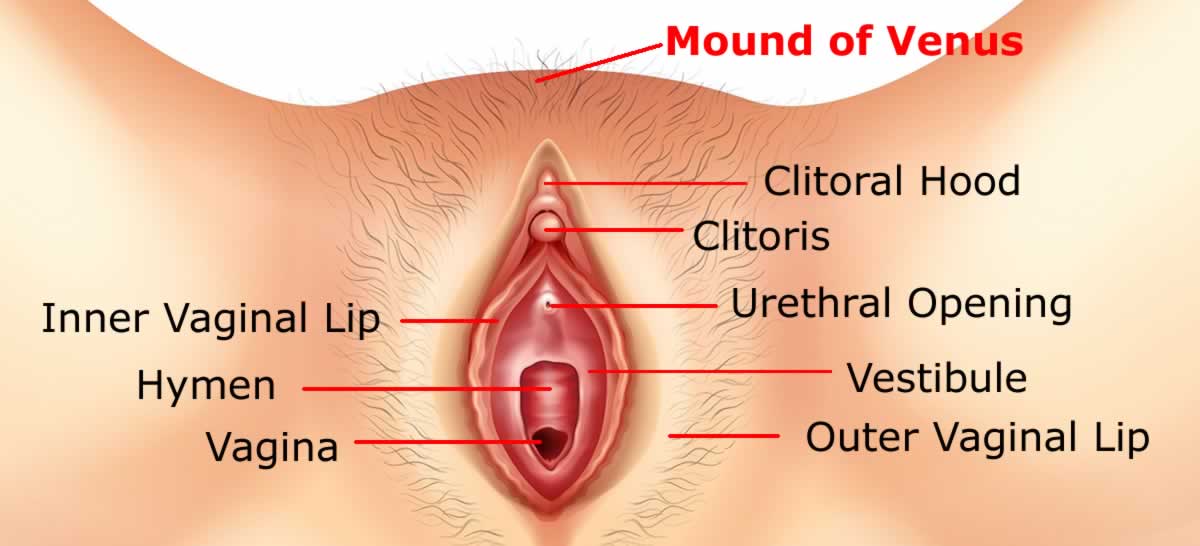
The mons pubis also called the mons veneris, or the mound of Venus, is the area over the pubic bone which is covered by a pad of fatty tissues and skin (Venus is the Roman goddess of love). This pad of tissue helps in protecting internal sexual and reproductive organs.
The skin over the mons pubis gets covered by pubic hair as the girl reaches puberty. The skin over mons pubis has numerous nerve endings, making this area highly sensitive to touch.
Caressing or even slight touch over this area can lead to sexual arousal, which some women find as pleasurable as touching clitoris.
Some women prefer to keep the hair as they are, whereas some prefer to trim them for esthetic look. Some prefer to remove the pubic hair to expose mons pubis and allow its direct contact with partner to experience different sexual pleasure.
| |  | External Sexual Organ - Outer Vaginal Lips (Labia Majora) | | |
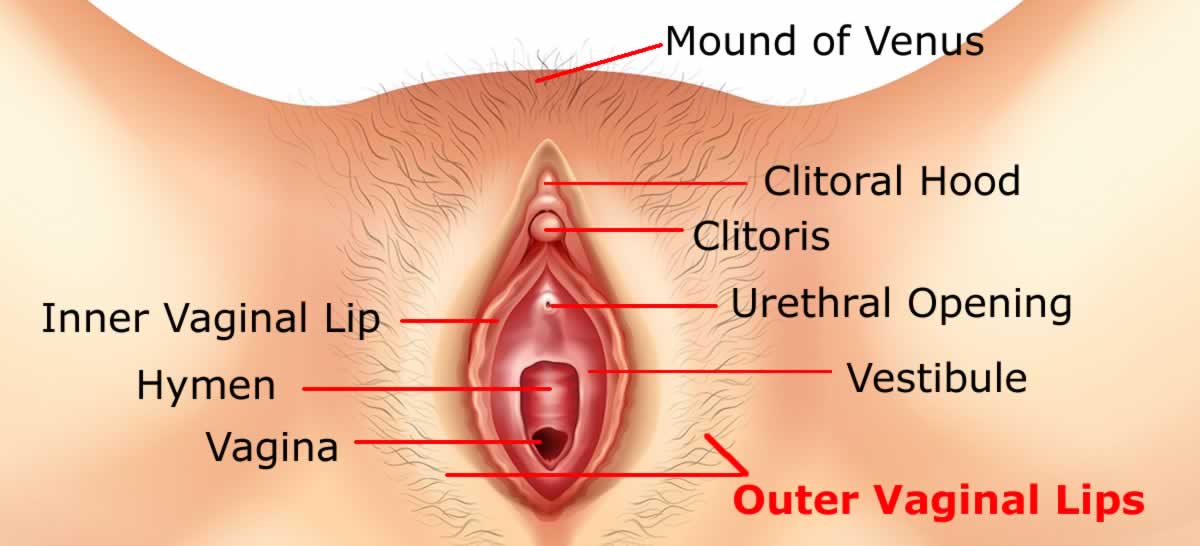
The Outer Vaginal Lips, called Labia Majora are two spongy folds of skin on either side of vaginal opening, which contain fatty tissues and thin layer of muscles.
There is liberal distribution of sweat glands, oil glands and nerve endings under the skin around these outer lips. On puberty this skin gets covered by pubic hair.
In a sexually unstimulated woman, these outer Lips remain folded and united in the midline to provide a covering and protection for urethral (urinary) and vaginal openings.
In sexually stimulated woman these outer lips flatten and open up to allow clitoris and inner lips and make the vaginal opening easily accessible to insertion of penis for intercourse.
| |  | External Sexual Organ - Inner Vaginal Lips (Labia Minora) | | |
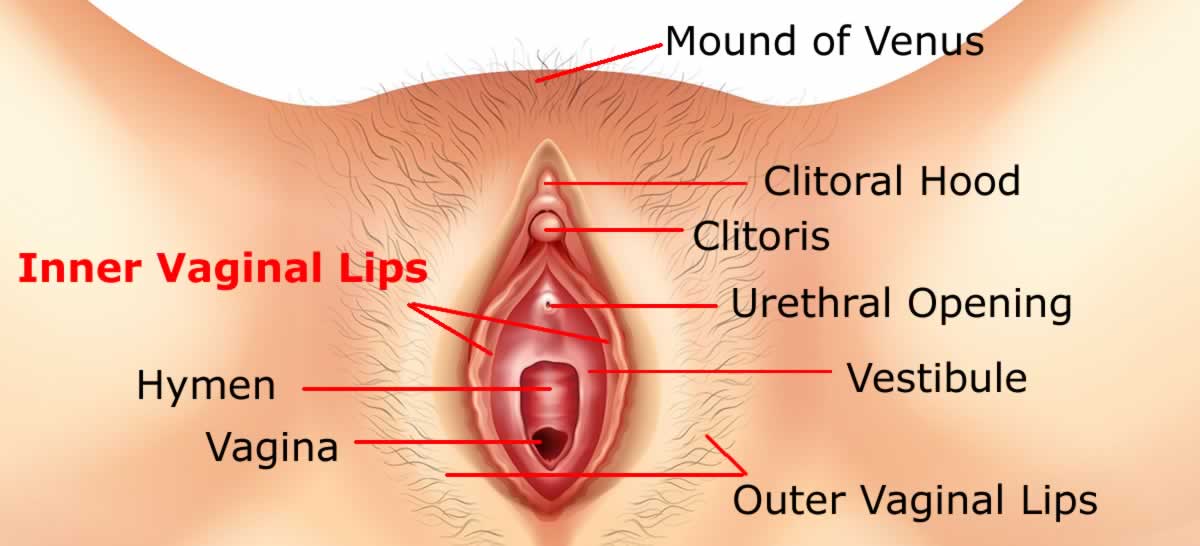
The Inner Vaginal Lips called Labia Minora are two erectile folds of skin placed inside the outer vaginal lips on either side of urethral and vaginal opening.
This petal-like structure has a core of spongy tissue rich in blood supply (capillaries), without any fatty tissues.
The skin covering inner lips have no hair on it but, are rich in nerve endings.
These inner lips meet above the clitoris creating a fold of skin called clitoral hood. This part of the skin sometimes referred as female foreskin.
Inner lips meet in the midline to cover the urethral (Urinal) and vaginal opening.
On sexual arousal, the inner surface of the lips become wet due to secretion from Bartholin’s glands.
Bartholin’s Glands are two small round glands placed on either side of vaginal opening (4 o’clock and 8 o’clock position) which secret a mucus like fluid during sexual arousal.
The ducts of these glands open on the inner surface of the inner lips next to vaginal openings.
On sexual arousal of a woman, these Bartholin’s Glands release few drops of secretion which keep the inner lips around vagina moist.
Although it was previously considered to facilitate vaginal lubrication during intercourse, it is now established that this secretion makes the vaginal opening moist (wet) to facilitate easier insertion of penis.
| |  | External Sexual Organ - Vestibule | | |
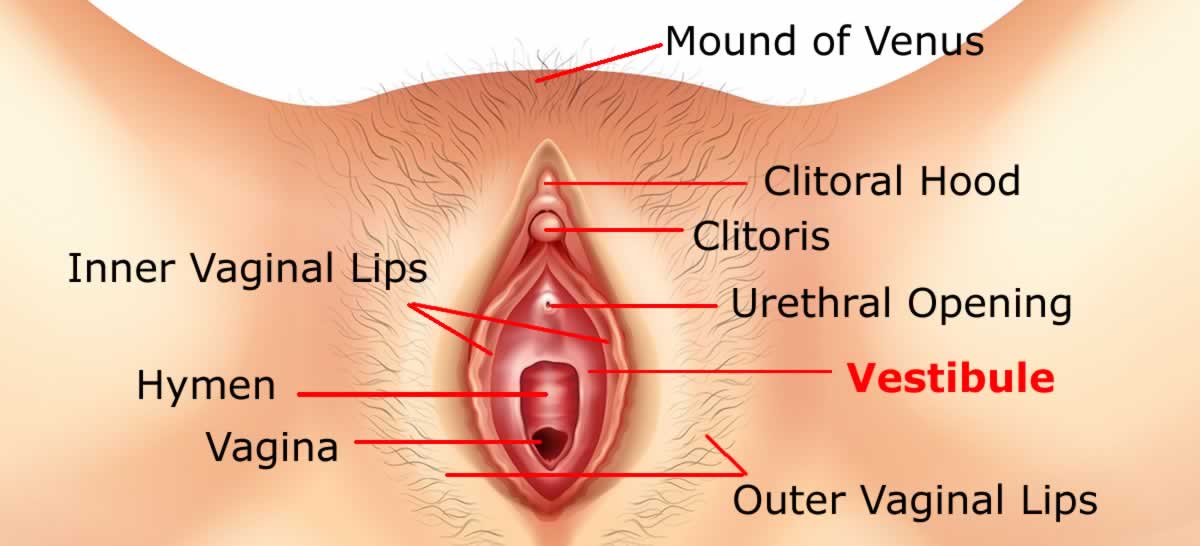
The area covered by the inner lips which includes vaginal and urethral opening along with Bartholin’s glands is called the vestibule.
The front ends of the inner lips meet above the clitoris to form a clitoral hood. The back end of the vestibule is where inner lips meet just before the perineum.
| |  | External Sexual Organ - Openings in Female Genital Area | | |

In the female genital area (groin region) there are three openings.
Vaginal opening: The largest being Vaginal opening which is flexible and designed to allow passage of Penis inside vagina during intercourse and passage of a baby from the uterus during its birth.
Urethral opening : The opening in front of vagina is called urethral opening which passes the urine out.
Anus: The other opening behind the vagina is anus which is the end of our digestive system which helps in excretion of feces.
The external Female genitals placed around vaginal opening are called vulva which includes Hymen, Clitoris, Inner Lips, Outer Lips and Mons Pubis.
| | 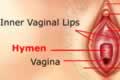 | External Sexual Organ - Hymen | | |
The opening of the vaginal canal is covered externally by a membrane called hymen. It may or may not be present at birth.
In some women hymen has tiny openings through which menstrual blood can easily pass. But, if the hymen is un-perforated, it may lead to accumulation of blood and disintegrated lining of womb (endometrium) during menstruation leading to pain and infection, requiring immediate medical intervention.
The natural hole or holes present in the hymen can also allow passage of sperm deposited on vulva. Hence, pregnancy is possible even when hymen is intact, and even when penis is not inserted inside the vagina; if semen is spilled over the vulva.
Sometimes hymen may be just a rim of tissue around vaginal opening and in some it folds naturally along the walls of vagina.
Covering of Hymen may break open at the time of first intercourse or at the time of puberty.
The remnants of this hymen are present in many women in the vestibule in the form of tags of skin even in their adulthood.
For many years and till date there is a general belief that presence of hymen is proof of virginity. This is not true. There are many instances like sports activities; insertion of tampons during menstruation or even masturbation can cause rupture of hymen.
If unbroken at the time of first intercourse, girl may experience pain and bleeding due to breaking of hymen. However this too cannot be a test of virginity.
In some, presence of hymen may resist insertion of penis, causing severe pain to both the partners. This problem can easily be solved by a gynecologist with the help of a simple procedure.
| | 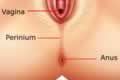 | The Perineum | | |

The perineum is the hairless area of skin between the bottom of the labia and the anus. This region being richly supplied by nerve endings it is highly sensitive to touch, temperature and pressure,
Touching of this area may induce sexual arousal.
Under the skin of perineum is the network of muscles which surround the vagina and placed between vagina and anus. These tough muscles of perineum support the pelvic cavity and helps in keeping pelvic organs in place.
| |  | Internal Sexual Organ - Vagina | | |
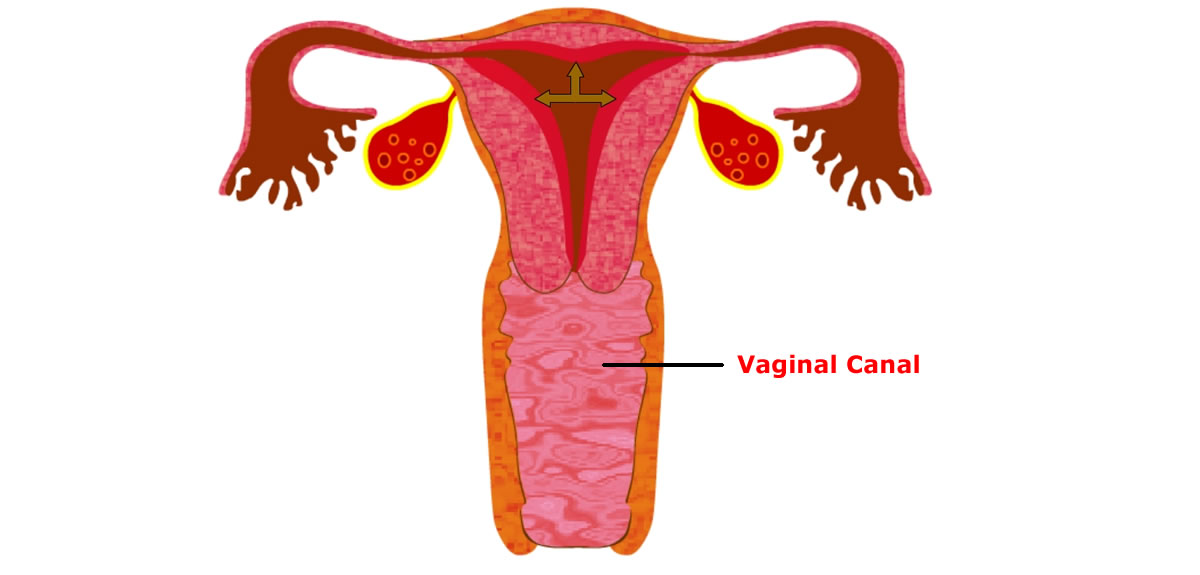
Vagina is the biggest opening in the genital area of a woman placed between urethral opening in front and anus behind.
The vaginal opening extends inside as a tubular passage up to the opening of Uterus, called cervix.
Vagina is about 3.5 to 5 inches in length and 1 to 2 inches wide and made of soft folds of skin.
Vagina is muscular and highly expandable passage which remains flat with its walls remaining gently in contact with one another.
Function of this vagina is to allow penetration of penis during sexual intercourse, and receive and store the semen ejaculated from the penis sufficiently to allow passage of sperms inside the uterus through opening in cervix.
Vagina also allows passage of menstrual fluid during menstruation and passage of baby during its birth.
The front inner wall of vagina is richly supplied by nerves which makes it more sensitive that the inner surface of the vaginal wall behind.
During the intercourse, vaginal walls provide immense sexual pleasure to woman, which results into repeated contraction of pelvic floor muscles extend better grip of penis making the intercourse mutually satisfying.
At Puberty
At puberty, walls of the vagina start producing a fluid which is thicker and stickier than saliva. This fluid keeps cleaning inner surface of the vagina. The environment of vagina is kept infection-free with the help of “good bacteria” present in this fluid. Many women notice the discharge of this fluid from vaginal opening when they are sexually excited or aroused, which is normal for any woman.
Discharge of this fluid from the vagina should not be the matter of concern unless it is giving bad odour, which indicates presence of some infection in vaginal area and calls for visit to a gynaecologist for advice.
| | 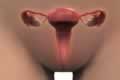 | Internal Sexual Organ - Adult Vagina | | |
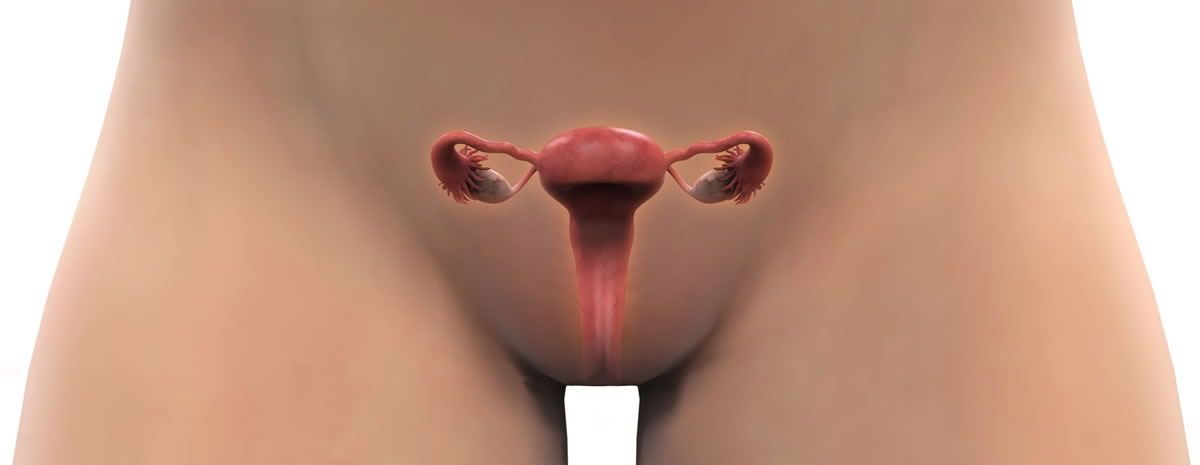
Adult vagina is very thick, strong, muscular and is able to expand to many times its normal size to allow passage of the baby from the womb during birth.
But, in young girls the vaginal walls are thin and cannot stretch so much as in adults. Therefore child birth during adolescence is dangerous as it can lead to tearing or bursting of vagina during child birth and may create a life threatening situation.
Vaginal opening in the groin region remains closed and covered by the folds of inner lips of vagina. These inner vaginal lips are covered by stronger folds of skin called outer vaginal lips.
Some people think that vagina is a continuously open space. This is not true. The walls of the vagina remain gently in touch with one another even though they have ability to expand as well as elongate. When something is placed inside vagina, like penis during intercourse or tampon during menstrual period, the walls of vagina accommodates it by moulding around it.
Just as vagina has ability to expand for accommodating passage of baby during birth, it has ability to elongate during intercourse to accommodate the erect penis.
The depth of vaginal passage from its opening in genital area to mouth of uterus i.e. cervix, is about 3 to 4 inches when woman is not sexually aroused. In some woman it may normally be even 5 to 7 inches in depth.
During arousal, the blood flow in the genital area increases; and with sexual excitement the upper two third (the back part) of vaginal passage elongates and forces the cervix and uterus to move further upwards.
| | 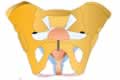 | Internal Sexual Organ - Uterus (Anatomy) | | |
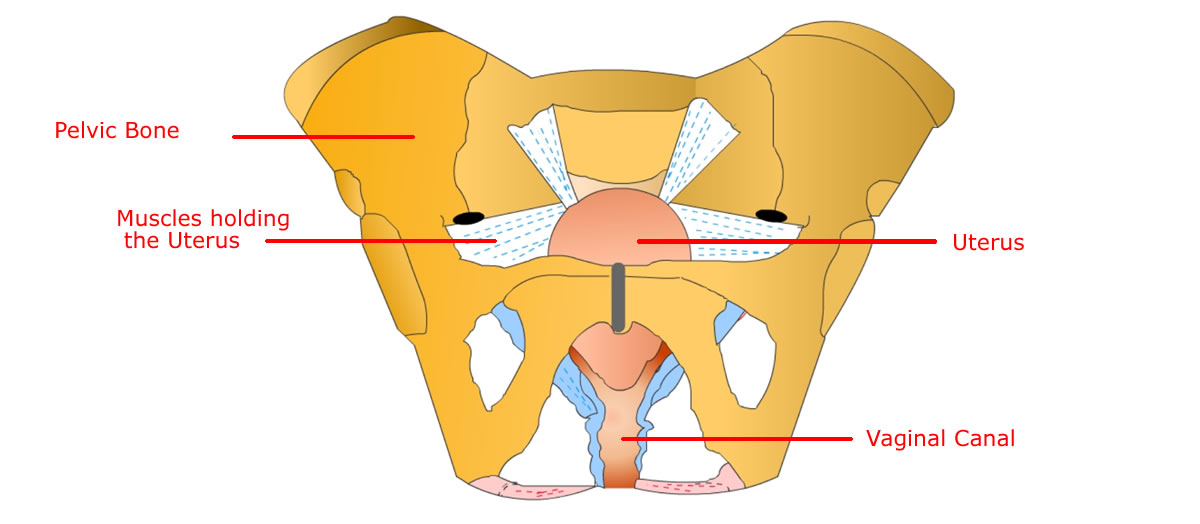
Uterus or the womb, is a hollow thick walled, pear shaped muscular organ located between the bladder and rectum.
Uterus is around three inches long and two inches wide
It lies suspended inside the space within hip (pelvic) bones with the help of very strong muscle fibres and ligaments and is supported below by pelvic floor muscles.
This strong support structure is designed to bear weight of the baby during pregnancy.
Uterus is made of two parts - a body called corpus and a neck called cervix.
The narrow end of the uterus which opens into upper end of vaginal canal is called cervix (neck).
On either side of its upper end, uterus extends into two hollow tubes called fallopian tubes where the fertilization of egg takes place. One of which carries a fertilized egg into the uterus to get embedded on the inner wall of uterus called endometrium, till it forms a baby.
Uterus is held loosely in the pelvic cavity by six ligaments. Although the angle of uterus varies person to person, in most women it is usually perpendicular to the direction (axis) of vagina.
| | 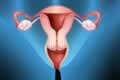 | Functions of Uterus (the womb) | | |
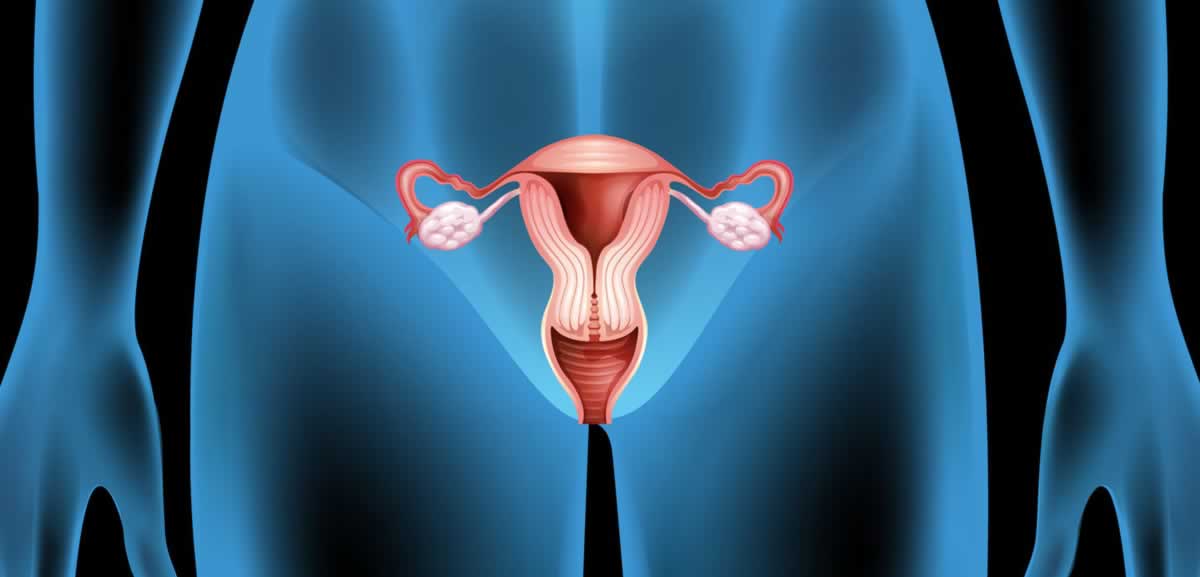
Every month the uterus forms a lining on the inside wall of uterus called endometrium, which facilitates embedding of fertilized egg and nourishment of embryo which grows in the fluid sac attached to the wall of the uterus, till the baby is fully formed for taking birth.
Myometrium or the muscle part of uterus facilitates carrying of baby during pregnancy and helps in labor and delivery of baby. Hormones released during pregnancy play a part in growth of uterus during pregnancy.
If the egg carried into the uterus is not fertilized or if the fertilized egg cannot get embedded on the wall of the uterus, the lining of the uterus gets disintegrated and comes out in the form of menstrual bleeding.
The upper part of the uterus contracts when woman experiences orgasm.
At birth this uterus is very small and has no lining. After puberty the uterus gets lined every month by an epithelial lining called endometrium which is required for holding the fertilised egg and to pass nourishment for the development of the baby.
If the egg is not fertilized this endometrium is shed along with unfertilised egg during menstruation and is slowly replaced in the course of next menstrual cycle.
Although the Reproductive System has direct access to outside, it is well protected from infection by the acidic mucous secretion.
This environment becomes alkaline during the fertile period for allowing sperms to enter the uterus.
| | 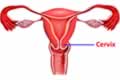 | Internal Sexual Organ - Cervix | | |
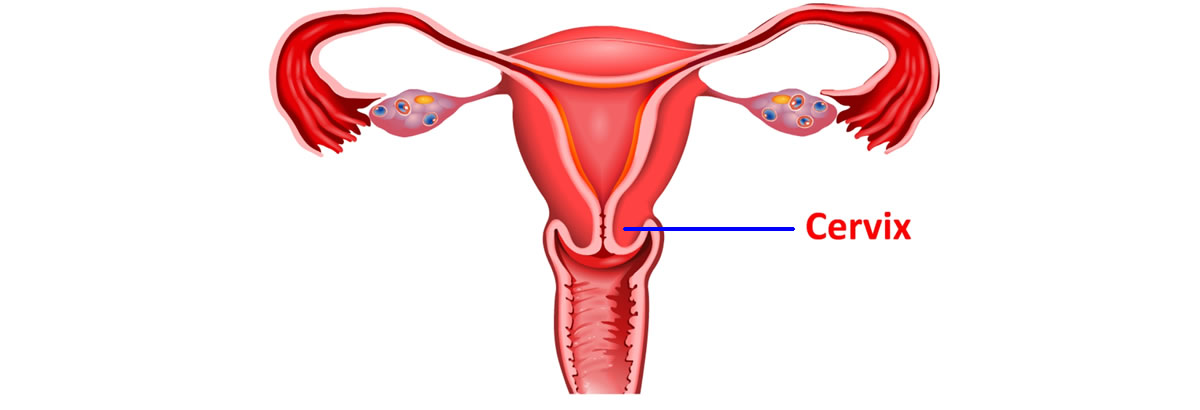
The Cervix is a cylindrical shaped part of uterus which projects into vagina. The cervix is about ‘1 inch’ long and has a fine canal (cervical canal) running through it which opens into the cavity of the uterus above and the vagina below. Its opening can also be felt easily by inserting the finger into the vagina.
The orifice or opening of cervix allows passage of menstrual flow from the uterus into the vagina.
This opening also allows passage of sperms into the uterus when the semen is deposited in the vaginal canal.
The opening of cervix is so narrow that only menstrual fluid or seminal fluid could pass through it.
Some men fear that during sexual intercourse if the condom slips off it may pass through opening of cervix into the uterus. This is impossible to happen.
Before the childbirth opening of uterus into the vagina is quite small and circular.
During the childbirth it stretches about 1000 times to allow passage of baby and after childbirth it reshapes into a small slit.
| |  | Internal Sexual Organ - Fallopian Tubes and Ovaries | | |
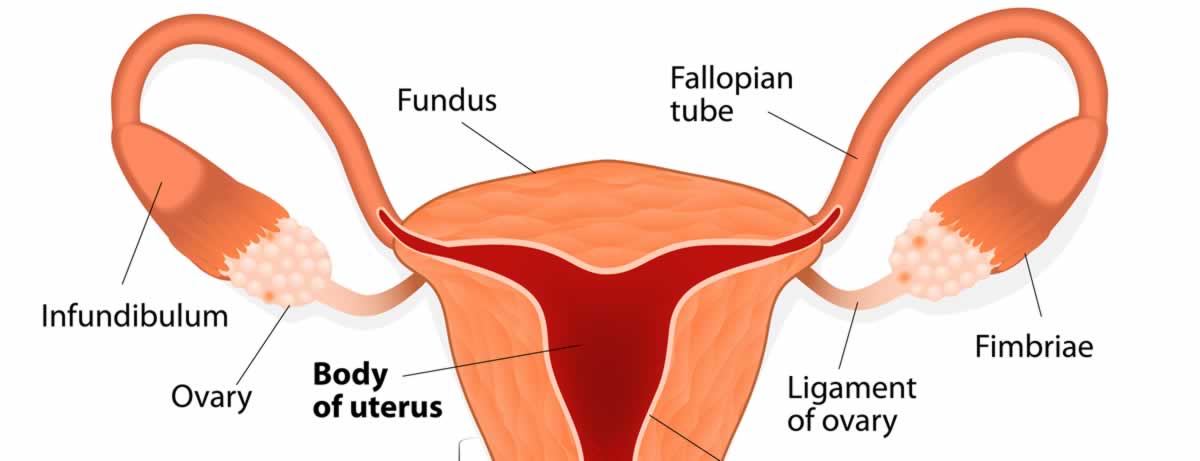
Fallopian Tubes or oviducts are pair of tubes which extend from either side of upper part of uterus and extend towards ovaries but do not touch them.
Each fallopian tube is of about 4 inches in length.
When the egg is ready in the ovary and is thrown out, the ends of the fallopian tube catches it. If the sperm travelling through vaginal canal, cervix, uterine cavity and cavity of the fallopian tube reaches the egg after its long journey within 3 to 4 days of egg’s presence in the end part of the fallopian tube, fertilization can take place.
The fertilized egg then develops further into multi-cell embryo by the time it reaches uterine cavity and is ready to get embedded on the endometrial lining specially formed on the inner walls of uterus to facilitate formation of baby.
If the sperms do not arrive for fertilization of egg or when woman does not have deposits of semen in the vagina, the unfertilized egg is carried to the uterine cavity only to be thrown out along with disintegrated endometrial lining of the uterine wall.
In most women one egg is released every month. If it does not get fertilized in a given time shedding of egg along with disintegrated endometrial lining happens every month in cyclic fashion, called Menstrual cycle or Period.
This fallopian tube is cut and tied as a procedure for permanent sterilization in women, so that sperms do not reach the matured egg for fertilizing it. The egg gets disintegrated within the fallopian tube and corresponding shedding of endometrial lining occurs as scheduled because there is no embryo to embed in its lining.
Ovaries are parts of female reproductive system which make an egg and release it for the purpose of fertilization.
These Ovaries are on either side of uterus tied to the walls of the pelvic bone with strong elastic fibres.
Girl becomes capable of bearing a child only when the ovaries begin formation of egg which is usually some months after the first menstruation.
Ovaries contain over 40,000 to 300,000 follicles at birth called Graafian follicle, each containing an immature egg. But, only 350 to 500 of follicles mature during fertile span of the woman and only a few get fertilised and develop into human beings. And, remaining disintegrates harmlessly inside the body.
Once egg is matured, the follicle enlarges and breaks open to release the egg. Only one matured egg (ovum) is released from ovary of one side at a time, once in a 28 day cycle, by a process called ovulation. The Ovum is 1 to 1.5 mm in diameter.
While the egg is getting ready for release the hormonal changes in the body form a lining inside the uterus to suit embedding of the fertilized egg. These hormones also create favourable environment for the fertilization to take place.
Ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone, the hormones responsible for development of sexual characteristics. These hormones help in elasticity and lubrication of genitalia.
Ovaries also produce Testosterone, although in small quantity, which is responsible for sexual desire in women.
| | |